 |  |
 |
| ||||||||
What is a web server certificate?
A certificate is a small file that uses cryptography to bind a public key to encrypt traffic to a website with the website’s ownership and identity details.
What is a certificate authority?
A certificate authority (CA) is an organization that has been established to issue digital certificates. To be trusted by web browsers and other web clients, certificate authorities are independently audited to ensure that they meet security requirements to protect the trust of the Internet community. When a CA issues a certificate for a web server, it signs the certificate with a digital hashing algorithm. This digital signature is used to prevent an attacker from impersonating the website. The certificate authority for SAP Ariba is DigiCert.
What is SHA1 and SHA2?
SHA2 (also known as SHA256) hash is much longer than the SHA1 hash and is therefore considered stronger cryptography. In 2014, a collective of certificate authorities and browser software developers called the CA/Browser Forum passed a resolution to deprecate SHA1 certificates in favor of SHA2 during 2016.
What is certificate pinning?
Some integrations with Ariba may use certificate pinning. In this case, the system interface that connects to the SAP Ariba Cloud systems trusts only a specific web server certificate and not just any valid web server certificate that is signed by a trusted certificate authority.
What is an RSA Certificate?
RSA is currently the industry standard for public-key cryptography and is used in most SSL/TLS certificates. RSA is not an acronym rather the name is a set of the first initials of the developers of the algorithm.
What is an ECC Certificate?
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) is an alternative encryption algorithm used for certificates. The type of certificate (ECC or RSA) is dependent on the configuration in the customer’s landscape.
How can you determine which certificate type you are using?
If you open the .crt file that is currently loaded in your system, look at the “Issued by” field. If it states “RSA” or “SHA256”, it is an RSA certificate
If it states “ECC” or “SHA384”, it is an ECC certificate.
What is a root, intermediate, and leaf certificate?
A certificate path contains the root, intermediate, and leaf certificates. If you open the .crt file that is currently loaded in your system, click on the tab Certification Path, to show the Root, Intermediate, and Leaf certificate.
The certificate on the bottom of the list is considered the leaf certificate. The next one up is the intermediate certificate. The top one is the root certificate.
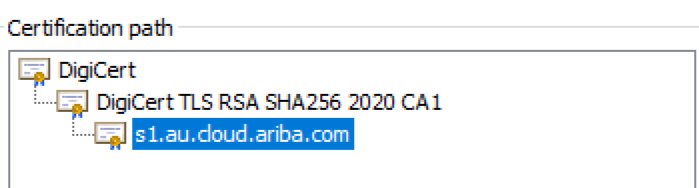
The leaf certificate is provided to the customer on SAP Ariba Connect. Depending on the customer’s configuration, it may be required to load the root and/or intermediate certificate in addition to the leaf certificate.
How can you obtain the root and intermediate certificate?
If you open the .crt file that is currently loaded in your system, click on the tab Certification Path, to show the Root, Intermediate, and Leaf certificate.
References
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC Certificates) | DigiCert.com